Crypto exchanges are the very center of the world of digital assets, handling massive volumes of transactions on a daily basis. Unfortunately, this makes them high-value targets for cyber threats such as phishing attacks, social engineering, re-entrancy attacks, and DDoS attacks.
To mitigate these, high-end exchanges employ solid security measures like multi-factor authentication, cold wallet custody, and real-time surveillance. With threats evolving more and more sophisticated, securing these platforms is key to maintaining user faith and industry integrity.
Popular tactics used by crypto hackers
Crypto exchange breaches are rarely simply an issue of sloppy code or outdated software. They often arise from a critical lack of specialized security expertise among blockchain developers and infrastructure teams. Behind each exploit is a carefully crafted combination of social engineering, technical ability, and human management, conducted by a professional engineer to hacking crypto exchanges.
More than just “bad code”
Crypto teams—high-speed, pseudonymous, and remote are often the aim for social hackers. Attackers create profiles of workers, impersonate executives or partners, and send urgent “admin” messages with malicious links to steal credentials or install malware. It only takes one misplaced click.
A Bitdefender Labs researcher was sent a LinkedIn message offering a job at a crypto exchange. The attacker responded with a demo project that contained hidden malware (cross-platform info-stealer). Upon running the demo, a stealthy script installed malware that stole browser passwords and crypto wallet keys. It is one of the most well-known crypto hacks 2025.
This cryptocurrency hacking was from the Lazarus Group, which has been associated with North Korea and is well known for targeting blockchain professionals with fake job offers to steal sensitive data and install persistent malware.
Social engineering masterminds
Contemporary hackers exploit protocol design weaknesses rather than brute force. They target:
- Unsecured withdrawal functions
- Re‑entrancy vulnerabilities
- Flash loan exploits
- Weak cross‑chain message verification
August 2021’s Poly Network cryptocurrency hack drained $610 million by exploiting cross‑chain logic weaknesses—specifically buggy Merkle proof verification and insecure keeper key management—without breaking encryption.
Technical exploits
Even with more than one security stack layer, it’s most often a small mistake that offers the gateway for cryptocurrency hacking.
It could be a developer putting secrets into a public repository, a stale 2FA (two-factor authentication) token that wasn’t terminated, or misconfigured access controls on cloud infrastructure. Security hygiene is typically lagging behind speed, and attackers already have the map: open-source codebases, stale Docker images, exposed API endpoints, or an errant IAM role usage.
Weaknesses in the human firewall
Crypto exchange hacks are usually the outcome of a series of weaknesses — one weak link in a chain of assumptions and workarounds. It’s a mix of psychological manipulations and systemic blind spots.
And while defenders have to anticipate each conceivable angle, attackers need only one opening to push the door wide open.
Fort Knox or digital sieve? Current security measures in play
Fort Knox is a U.S. military installation that’s supposed to store a ginormous hunk of America’s gold reserves, and be basically break-in-proof. In cryptocurrency, it’s a symbol used metaphorically for super-tight security. But with crypto exchanges, the question is: are their defenses really Fort Knox-grade, or like a digital sieve, full of holes?
Industry standard defences
Most reputable crypto exchanges have implemented at least industry-standard protections against blockchain hacks:

- Cold wallet storage User funds are kept offline, inaccessible via internet-connected infrastructure.
- Multi-signature wallets One compromised key cannot empty the funds.
- 2FA & MFA (two-factor authentication & multi-factor authentication) Required for both user logins and internal admin activities.
- Withdrawal whitelisting Prevents attackers from sending funds to arbitrary wallets.
- KYC (know your customer) verification Ensures only verified users can access the platform, helping prevent fraud and comply with regulations.
The reasons why blockchain hacks still occur
Despite these defences, breaches still happen. Why? They can occur due to the following reasons:
- Excessive trust in perimeter security After getting inside the network, many systems still trust the actor too much. Little microsegmentation or internal monitoring exists.
- Hot wallet exposure Certain exchanges keep an excessive amount of funds in hot wallets for liquidity, which makes them fat targets.
- Unreliable key management Some smaller or fast-growing exchanges still use insecure storage or bad rotation practices.
- Third-party risk APIs, plug-ins, and third-party service providers are under-secured or over-permissioned.
Emerging smarter security measures
Leading exchanges are beginning to adopt stronger, more intelligent methods such as:
- Hardware security modules (HSMs) Physical devices that securely create and store private keys.
- Threshold signature schemes (TSS) A сryptographic technique of sharing a signing authority without the typical multisig limitations.
- Continuous threat monitoring & red teams Simulated attacks to actively uncover blind spots.
- Zero trust architectures (ZTA) Everything on users and services is authenticated wherever they reside.
The trade-off of compliance vs. security
A major standoff is between security and compliance. Compliance schemes are typically lagging behind current attack vectors, with transactions technically “compliant” but vulnerable.
Security teams, on the other hand, are stretched to the limit, forced to balance getting product out the door versus hardening systems up.
Fort Knox or digital sieve?
Some exchanges are actually Fort Knox-grade — using multi-layered security, in-built audits, and top-notch cryptographic custodial. Others are still operating like it’s 2017 — with burning hot wallets out in the open and access controls strapped with duct tape.
The human element: Empowering your users in the fight
Nothing short of backend security best practices can prevent users from clicking on phishing links or revealing credentials. Your users are your attack surface as an exchange operator.
Developing user-empowering security features, paired with education, cuts risk of breach in half.
- Bake transaction alerts, dApp connection warnings, and URL spoofing detection into the UI (user interface).
- Offer built-in phishing link scanning within in-app notifications or messages.
- Provide bespoke security dashboards showing account risk (IP flips, login attempts, and others).
You’re the first line of defense
Every node operator, developer, and ops engineer on your team is holding keys to the kingdom—literally. Take an internal Zero Trust mentality:
- Disable SSH (traditional access using static passwords or private keys) for keyless or ephemeral certificates (for example, via HashiCorp Vault or Teleport).
- Use hardware-backed YubiKey authentication for admin consoles and CI/CD pipelines.
- Audit admin wallet activity through tamper-proof logging (for example, use immutable logging through Merkle tree structures).
Wallet wisdom: Designing custody responsibly
Bad crypto wallet handling is responsible for the majority of 9-figure crypto hacks (losses of $100 million or more). Below you can see some suggestions to protect your crypto exchange:
- Use MPC (multi-party computation) or TSS for hot wallet transactions. This discharges single-point-of-failure risk without annoying multisig UX (user experience).
- Cycle withdrawal wallets and set time-based constraints per asset, per user, per address.
- Consider geofencing withdrawal requests and biometric authentication for mobile apps withdrawals above certain thresholds.
The scammers’ catch and how to avoid them
Social engineering most often bypasses tech entirely. Here are helpful defence measures:
- Enforce multi-party approval processes on risky activities like contract upgrades, off-chain transactions, or provisioning of access.
- Use real-time behavioral analysis to detect outlier activity in developer or ops behavior (for example, access outside of standard hours, shady Git behavior).
- Perform regular internal phishing simulations for employees and approved project accounts.
Internal team personal security hygiene
It is important to ensure robust protections on every device and workflow:
- Enforce per-device app allowlisting on DevOps and wallet teams.
- Add hardware-backed 2FA on all workstations and cloud consoles.
- Integrate secrets managers (Doppler, Vault) seamlessly into CI/CD pipelines—never hardcode API keys or secrets.
- Implement endpoint detection and response (EDR) agents on all corporate devices, even for remote employees.
Beyond the breach: The future of crypto security
Cryptosystems cannot be pieced together with patchwork defences. These systems demand proactive, resilient strategies built for the future.
The evolving crypto threat landscape
Keep in mind that crypto exchange hack strategies are becoming more targeted and technical. Today’s threats go far beyond just phishing:
- Lazarus-style campaigns are targeting DevOps via spoofed LinkedIn job opportunities. These are malware-based on “project demos” or PDFs.
- Smart contract logic vulnerabilities, rather than bugs, are being exploited (e.g., lack of reentrancy guards, unvalidated return values).
- Cross-chain crypto hacking attacks are becoming more prevalent—poor bridge verification and the absence of proper message signing logic are typically the culprits.
Modern security solutions
Top-tier crypto orgs use advanced, modular security architecture built for resilience and speed.
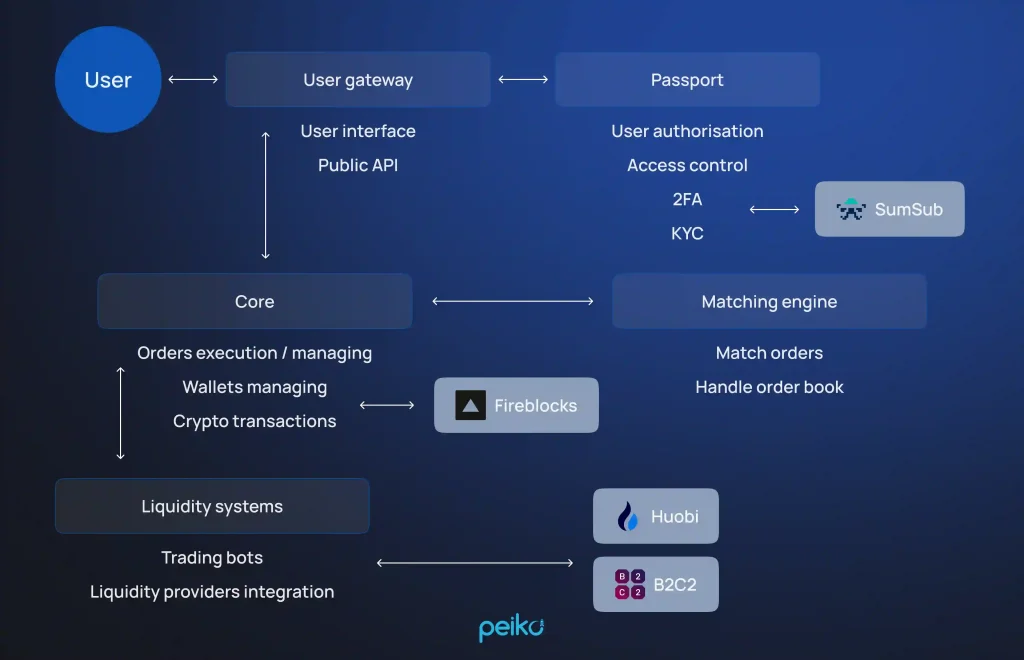
- Cold wallet key management using air-gapped HSMs (Fireblocks, GK8, etc.).
- Modular layers of security: isolate authentication, signing, custody, and compliance services into interdependent microservices.
- Bug bounty integration in your SDLC through Immunefi or Code4rena, tightly integrated with your PRs and CI/CD.
- Security chaos testing: Simulate wallet key breaches, oracle feed outages, or cross-chain congestion using internal red teams or automated tools.
The role of regulation and collaboration
Security is not only tech, security is trust. Transparency and collaboration are your best allies.
- On top of meeting standards like SOC 2, ISO 27001, or MiCA, publish public incident reports and post-mortems to build credibility.
- Share threat intelligence proactively with peers on platforms like MISP or ThreatConnect.
- Join industry security groups like Crypto ISAC or blockchain-specific working groups to improve sector-wide defense.
Shared responsibility
Secure cryptocurrency exchanges aren’t built— they’re sustained with continuous coordination:
- Dev teams: Integrate security checks into code, not just pre-launch.
- Ops: Screen infrastructure updates like code—versioned, reviewed, and traceable.
- Compliance: Work hand-in-hand with security, not after the fact.
- Users: Give them tooling and feedback mechanisms (withdrawal cooldowns, email verification, etc.) in order to participate in security, not just consume it.
Start your crypto exchange project securely
Launch your own cryptocurrency exchange quickly with our solid white-label platform, designed for reliability, scalability, and strong security.
Our white-label solution for crypto exchanges offers not only professional trading capabilities, high-volume liquidity, and advanced user experience, but also robust security features for high protection against crypto exchange hack.
- DDoS protection There are several internal and external protection steps taken so that the platform stays up and running during DDoS attacks, proven through rigorous stress testing.
- 2FA + KYC Access and withdrawals are protected through Google Authenticator 2FA, with optional SMS or email verification for added security.
- Fireblocks custody User funds are insured by Fireblocks, a well-established institutional custodian with a flawless security record.
- Encrypted data storage All user and system sensitive information is hashed and encrypted so that unauthorized access is not possible.
- Modular microservices architecture The operations are kept in separate, independent packages that contain risk and are easier to update and maintain.
- Autoscaling system The platform auto-scales with users, offering stable performance with zero downtime.
You can obtain this robust crypto exchange in 3 weeks, ready to go live. Custom functionality and extensions are also offered to tailor the platform to your precise needs.
Conclusion
As flash loan crypto hacks and sophisticated phishing attacks rise, deep security layers are essential. Our white-label crypto exchange platform includes integrated protection against cryptocurrency hacks such as 2FA, DDoS protection, encrypted storage, and Fireblocks custody to secure your users’ funds. Added to an auto-scaling infrastructure to handle growth with ease, it’s a modern crypto exchange solution.
Ready to hit the market in an instant and secure? We can launch your exchange online in as few as 3 weeks, with customizable options to address your unique needs.
Contact us now to get your crypto exchange with top-of-the-line defences.
FAQ
No one is 100% secure from cryptocurrency hack, but exchanges such as Kraken and Bitstamp have had clean slates with no reported breaks to date. Their robust security architecture and operational discipline have prevented them from suffering incidents to date.
Most exchanges have two-factor authentication (2FA) against cryptocurrency hacks, more often through authenticator apps rather than SMS. Other protections like cold storage, KYC verification, and whitelisting of devices/IP addresses are also prevalent.
If a cryptocurrency hack occurs, platforms typically halt withdrawals and trading, conduct a forensic audit, and reimburse affected users if reserves or insurance allow. Without sufficient protection, clients may lose their funds irretrievably.
The cutting-edge security is multi-layered: offline storage with MPC wallets or hardware, tight role-based access control, regular code and infrastructure audits, and real-time threat scanning. Internal teams and end-users are just as important as good code in being educated.









